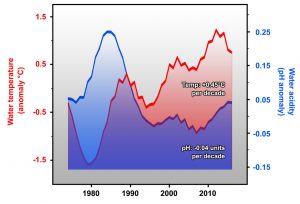
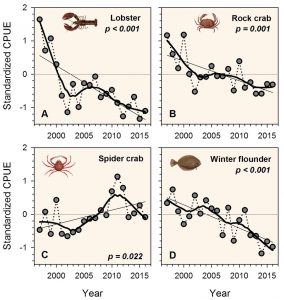
On October 17-19, 2018, six graduate students from Department of Marine Sciences participated in the first ocean expedition course ever offered by the university. Students have long lobbied for a course that teaches ship-based oceanographic methods, and after much logistical and scientific preparation by faculty, staff, and students, the team set sail aboard the R/V Connecticut. The objective of the cruise was to sample oceanographic data from Long Island Sound outwards to the continental shelf break. The team was led by Professors Jim O’Donnell, Frank Bohlen, Samantha Siedlecki, and Hannes Baumann, with research support from Kay Howard-Strobel and David Cohen. The student participants were Molly James, Jimmy deMayo, Alec Shub, Michael Mathuri, Amin Ilia, and Callie Concannon.
The course was designed to give students a chance to experience data collection aboard a research vessel from all oceanographic disciplines. Students oversaw around-the-clock deployment of CTD/rosette casts, sediment grabs/cores, Methot net trawls, and vertical plankton tows at a total of 7 stations. On board the ship, students analyzed pH and prepared samples for later analysis. Unfortunately, weather conditions limited the trip to just 36 hours instead of the intended 48 hours, but the team still managed to collect the data they intended to analyze. With the help of Dr. Claudia Koerting, students used analytical spectroscopy techniques to measure dissolved oxygen, nutrients, and chlorophyll concentration. After all the data was analyzed, the final cruise report was constructed, and the results were presented the following semester at the weekly Brown Bag seminar series hosted by the Marine Sciences Graduate Students. This course provided students with great hands-on experience and introduced the students to areas of oceanography previously beyond their knowledge levels.
To access all the data that was collected during the expedition, log on to ftp://nopp.dms.uconn.edu/ocean_course.
The graduate student class with faculty
Nighttime sampling station
Jimmy deMayo