Fall 2021 Department Achievements
Awards
Prof. Hans Dam
Received the 2021 UConn Faculty Excellence Award for Graduate Teaching. This Award recognizes a faculty member with a distinguished record of sustained teaching excellence through outstanding instruction, engaging students thoroughly in the process of learning, and contributing significantly to the intellectual life of the University.
Grants
CIRCA – Prof. James O’Donnell
The Connecticut legislature’s 2021-23 budget provided an additional $5 million to CIRCA to expand Resilient Connecticut activities and advance fundable projects. CIRCA will continue to support development of innovative adaptation approaches for flood and heat vulnerability along with expert advice on climate issues to communities in Hartford, New London, and Middlesex Counties.
Prof. Hannes Baumann
Connecticut SeaGrant: PI Baumann together with collaborators from CTDEEP received funding to investigate the causes and ecosystem consequences of the recent, steep increase in Black Sea Bass in Long Island Sound.
Jo-Marie Kasinak (graduate student, Prof. Vaudrey) & Prof. Vaudrey
Connecticut SeaGrant: Toward a deeper understanding of human connections with ocean environments: Ocean Identity (OI) as a novel construct, research instrument, and assessment tool. (2022-2024), $143,309, PIs Kelly, Kasinak, McKinley, Vaudrey, & Mattei.
Prof. Robert Mason
NSF Chemical Oceanography: Methylated mercury sources and cycling in the high latitude North Atlantic. (2021-2023), $283,534, PI Mason.
Prof. Samantha Siedlecki
NSF: Regional climate change projections to enable equitable ocean planning for the blue economy (2021-2022), PIs. Pinsky, Hice-Dunton, Siedlecki, & St. Martin. This project aims to enable climate-ready, coordinated, and inclusive decision making throughout the blue economy and spark a new generation of durable blue development.
Prof. Vlahos
NSF: Arctic Marginal Ice Zone Alkalinity (AMIZA). PI Vlahos. This project is studying the components of carbonate alkalinity in the changing Arctic with a focus on the transient ice melt zones.
NIH: Chronic Kidney Disease. PI Vlahos. Lead PI Shuchi Anand, Stanford University. This project is a continuation of our efforts with colleagues in Sri Lanka and at Stanford to expand our 300 person cohort to a 900 person longitudinal study on the progression of kidney disease and water quality.
Publications
Prof. Peter Auster
Prof. Auster presents a chapter as part of an international effort to inform delegations to the United Nations about the status and effects of human activities on the global ocean. (Levin, L. A., Auster, P., Clark, M. R., Hall-Spencer, J. M., Hopcroft, R., Ingels, J., Metaxas, A., Narayanaswamy, B., Tuhumwire, J. T., Yasuhara, M. (2021). Continental slopes and submarine canyons. Chapter 7J, p. 395-420, in: The Second World Ocean Assessment, World Ocean Assessment II. United Nations, New York.)
Prof. Auster addresses the confusion in ecological terminology used in international agreements to manage fisheries impacts on the high seas. (Watling, L., Auster, P. J. (2021). Vulnerable marine ecosystems, communities, and indicator species: confusing concepts for conservation of seamounts. Frontiers in Marine Science 8:622586.)
Prof. Auster and colleagues demonstrate that simple GoPro cameras can be used to quantify the role of oyster aquaculture cages as fish habitat. (Mercaldo-Allen, R., Clark, P., Liu, Y., Phillips, G., Redman, D., Auster, P. J., Estela, E., Milke, L., Verkade, A., Rose, J. M. (2021). Exploring video and eDNA metabarcoding methods to assess oyster aquaculture cages as fish habitat. Aquaculture Environment Interactions 13:277-294.)
Prof. Paola Batta-Lona
Prof. Batta-Lona and colleagues examined how environmental conditions affect the distribution of zooplankton in the Gulf of Mexico. (Cicala, F., Arteaga, M., Herzka, S., Martinez, M., Hereu, C., Jimenez Rosenberg, S. P. A., Saavedra, A., Robles, J., Gomez, R., Batta-Lona, P. G., Galindo Sanchez, C. E. (2021). Environmental conditions drive zooplankton community structure in the deep-water region of the southern Gulf of Mexico: a molecular approach. Molecular Ecology.)
Prof. Batta-Lona and colleagues used DNA (metabarcoding) to look at the diversity of zooplankton in the Gulf of Mexico. (Martinez, M., Hereu, C., Galindo Sanchez, C. E., Arteaga, M., Batta-Lona, P. G., Saavedra, A., Robles, J., Jimenez Rosenberg, S. P. A., Herzka, S. (2021). Epipelagic zooplankton diversity in the deep water region of the Gulf of Mexico: A metabarcoding survey. ICES Journal of Marine Science.)
Prof. Zofia Baumann
Prof. Baumann and colleagues present a study that demonstrates the liver detoxifies previously-bioaccumulated methylmercury based on analyses of tissues from three waterbird species. (Poulin, B.A., Janssen, S.E., Rosera, T.J., Krabbenhoft, D.P., Eagles-Smith, C.A., Ackerman, J.T., Stewart, A.R., Kim, E., Baumann, Z., Kim, J.H. and Manceau, A., 2021. Isotope fractionation from in vivo methylmercury detoxification in waterbirds. ACS Earth and Space Chemistry, 5(5), pp.990-997.)
Prof. Ann Bucklin
Ann Bucklin, chair of the Scientific Committee for Ocean Research (SCOR) Working Group WG157 presents with other members of WG157 a review paper examining global patterns of biodiversity of marine zooplankton using DNA barcodes or short sequences of cytochrome oxidase I (COI) that discriminate and identify species and announce a reference database for identification of species from DNA barcoding and metabarcoding of pelagic biodiversity, with advanced search functions by ocean region and taxonomic group. (Bucklin A., Peijnenburg, K. T. C. A., Kosobokova, K. N., O’Brien, T. D., Blanco-Bercial, L., Cornils, A., Falkenhaug, T., Hopcroft, R. R., Hosia, A., Laakmann, S., Li, C., Martell, L., Questel, J. M., Wall-Palmer, D., Wang, M., Wiebe, P. H., Weydmann-Zwolicka, A. (2021). Toward a global reference database of COI barcodes for marine zooplankton. Marine Biology.)
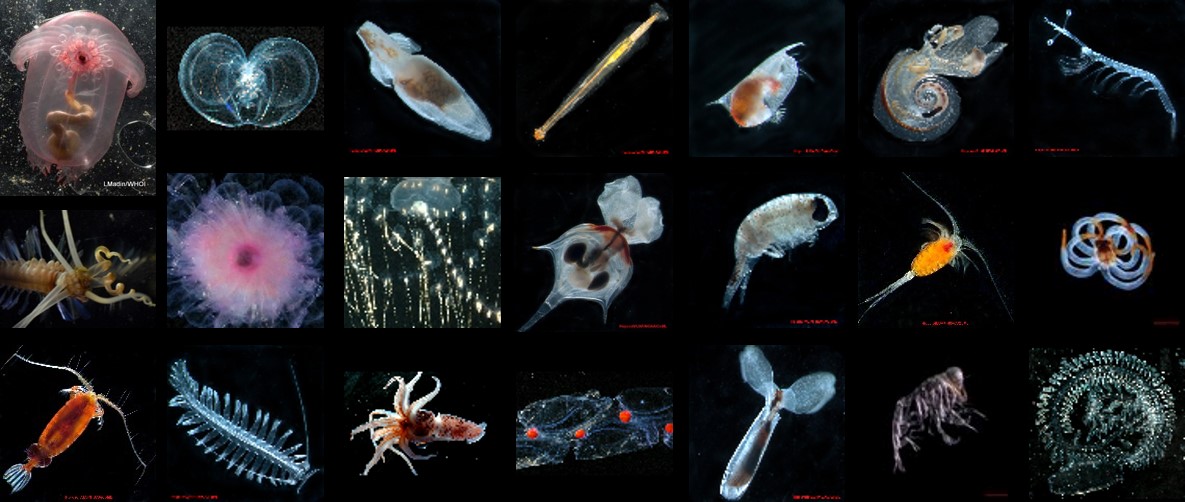

Photo by R.R. Hopcroft and C. Clarke (UAF) and L.P. Madin (WHOI); see: http://www.cmarz.org/galleries.html
Profs. Hans Dam, Michael Finiguerra, Hannes Baumann
Profs. Dam, Finiguerra, and Baumann show that zooplankton adapt quickly, but with limited capacity, to ocean warming and acidification, which is both encouraging and sobering news for the response of animal populations to rapid climate change. (Dam, H. G., deMayo, J. A., Park, G., Norton, L., He, X., Finiguerra, M. B., Baumann, H., Brennan, R. S., Pespeni, M. H. (2021). Rapid, but limited, zooplankton adaptation to simultaneous warming and acidification. Nature Climate Change, 11, 780-786.)
Prof. Leonel Romero
Prof. Romero and colleagues propose a new approach to realistically model wave effects on currents, overcoming several limitations of state-of-the-art coupled wave-ocean models. (Romero, L., Hypolite, D., McWilliams, J. C. (2021). Representing Wave Effects on Currents. Ocean Modelling, 167, 101873.)
Prof. Sandy Shumway
Prof. Shumway edited a book titled “Molluscan Shellfish Aquaculture: A Practical Guide” as a usable manual for those interested in an up-to-date introduction to the field. The book covers each of the major cultured species of cultural importance. (Shumway, Sandy, Ed. (2021) Molluscan Shellfish Aquaculture: A Practical Guide. 5M Publishing.)
Prof. Samantha Siedlecki
Prof. Siedlecki and colleagues present work showing that the projected changes for carbon variables like pCO2 and pH in the California Current System (CCS) using a high resolution model are modified by coastal processes resolved in the downscaled projections relative to the projected global simulation, suggesting downscaled projections are necessary to more accurately project future conditions of these variables. (Siedlecki, S. A., Pilcher, D., Howard, E. M., Deutsch, C., MacCready, P., Norton, E. L., Frenzel, H., Newton, J., Feely, R. A., Alin, S. R., Klinger, T. (2021). Coastal processes modify projections of some climate-driven stressors in the California Current System, Biogeosciences, 18, 2871–2890.)
Prof. Siedlecki, graduate student Kelly McGarry, and colleagues present a combination of regional high-resolution simulations that project ocean acidification (OA) conditions for the Gulf of Maine into 2050, the results of which indicate that the aragonite saturation state (one measure of OA) declines and the entire GOM will experiences biologically critical conditions for most of the year. (Siedlecki, S. A., Salisbury, J., Gledhill, D. K., Bastidas, C., Meseck, S., McGarry, K., … & Morrison, R. (2021). Projecting ocean acidification impacts for the Gulf of Maine to 2050: New tools and expectations. Elementa: Science of the Anthropocene, 9(1):00062.)
Prof. Penny Vlahos
Prof. Vlahos, graduate student Emma Shipley, and colleagues present an interdisciplinary study that connects drinking water quality to the progression of kidney disease in rice farmers in the Sri Lankan dry zone. (Vlahos, P., Schensul, S., Anand, S., Shipley, E., Diyabalanage, S., Hu, C., Ha, T., Staniec, A., Haider, L., Schensul, J., Hewavitarne, P., Silva, T., Chandrajith, R., Nanayakkara, N. (Accepted). Water Sources and Kidney Function: Investigating Chronic Kidney Disease of Unknown Etiology in a Prospective Study. NPJ Clean Water.)
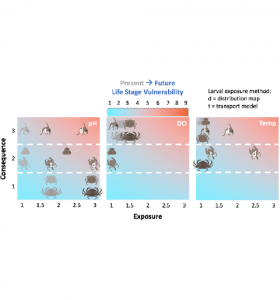
Halle Berger (graduate student, Profs. Samantha Siedlecki and Catherine Matassa)
Berger and colleagues present a vulnerability assessment for Dungeness crab to climate change which revealed that population-level vulnerability to future hypoxia is most severe overall due to increased exposure of the critical adult stage during the upwelling season. (Berger, H. M., Siedlecki, S. A., Matassa, C. M., Alin, S. R., Kaplan, I. C., Hodgson, E. E., Pilcher, D. J., Norton, E. L., Newton, J. A. (2021). Seasonality and life history complexity determine vulnerability of Dungeness crab to multiple climate stressors. AGU Advances, 2, e2021AV000456.)
Tyler Griffin (graduate student, Prof. Evan Ward)
Griffin and colleagues demonstrate that antibiotics can be used as effective tools to experimentally diminish the gut microbiomes of suspension-feeding animals, like oysters and mussels. (Griffin, T. W., Pierce, M. L., Nigro, L. M., Holohan, B., & Ward, J. E. (2021). An examination of the use of antibiotics as a method to experimentally perturb the microbiota of suspension-feeding bivalves. Invertebrate Biology. e12352.)
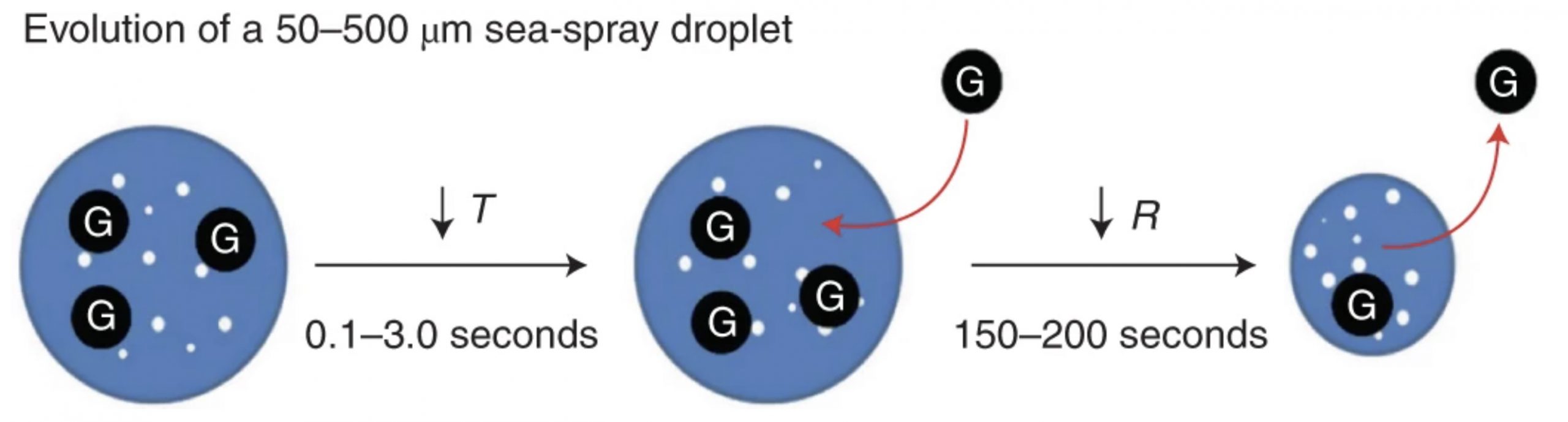
Allison Staniec (PhD graduate, Prof. Penny Vlahos)
Staniec and colleagues present a study identifying the role of sea spray in gas exchange in an article that was also featured in Nature Highlights: Big Potential for Tiny Droplets. (Staniec, A., Vlahos, P., Monahan, E. C. (2021) The role of sea spray in atmosphere-ocean gas exchange. Nature Geoscience, 14, 593-598.)